upper urinary tract
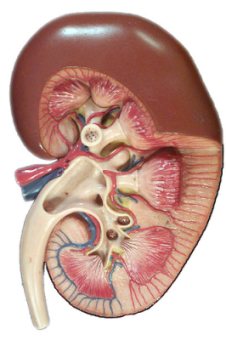
Acute renal failure : loss of kidney function, attributable to various causes, the most frequent being viral or toxic. The cat vomits, loses appetite and therefore decreases weight. His breath takes on a bad urinary odor, because, unable to expel nitrogen with the kidneys, he does so with breathing.
chronic renal failure : it is a progressive loss of use of the kidneys, the causes can be multiple. Quite often the affected cat begins to drink much more frequently and urinate accordingly. It is advisable, especially in elderly cats, to periodically check blood and feces, to attack the problem in the bud.
glomerulonephritis : kidney inflammation sometimes accompanied by viral forms such as viral leukemia and feline viral immunodeficiency. The subject does not have any striking symptoms, initially he is just a little apathetic, but over time he vomits, drinks more and has diarrhea.
polycystic kidney (PKD) : disease that has a genetic origin. Frequent in Persians, Himalayans and in crossings. They are cysts with liquid content present in the kidneys, the subjects have no symptoms.
lower urinary tract
cystitis and uteritis : they have quite similar symptoms. The main ones are the difficulty and pain in excreting urine, frequent elimination of small quantities of them, often hemorrhagic. The cat is very restless, it often approaches the litter box putting itself in the typical position it assumes when it wants to fool but to no avail. The most common causes are viral and bacterial. bladder stones : Persistent inflammation of the bladder. Diagnosis is made by ultrasound examination and therapy can be medical or surgical depending on the volume of the uroliths.