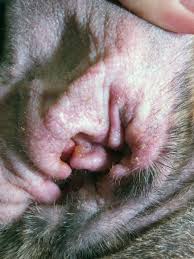
external earings
External earings can be twofold:
parasitic : supported by acres, which pass from cat to cat. Symptoms may manifest as intense itching or the presence of brownish-colored earwax.
bacterial : more rare, they manifest themselves with similar symptoms, but with less intense itching.
internal earings
cause head deviation, strabismus and inability to coordinate movements.
polyps
They are formations that form in the external auditory canal, they can be caused by chronic otitis. They cause strong secretion from the ear and/or nose.
auricular cancer
It mainly affects white cats over the age of eight. It manifests itself first on the margins of the auricles and then spreads rapidly in the surrounding tissues.
deafness
It may be the result of untreated chronic ear infections. In white cats with blue eyes, however, it can be congenital. In elderly specimens, sometimes, it occurs as a consequence of sclerotic or degenerative phenomena of the middle and inner ear.